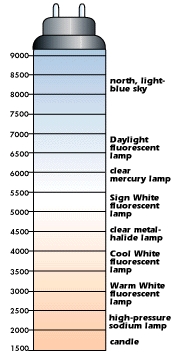
About Light sources and LED
Traditionally, light sources can be divided up in to the following categories:
- Light bulbs
- Halogen lamps
- Gas-discharge lamps
- Fluorescent lamps
- Special light sources and electrodeless lamps
- LED
LED is starting to play a more important role in contemporary times. More on this later.
Light bulbs
The German watchmaker Johan Heinrich Goebel came up with the light bulb in 1854. Thomas A. Edison then repurposed the idea in to a consumer product in 1879. The light in the light bulb originates from an electric current that sparks up a tungsten wire. About 5% of the electric energy is converted in to light. The rest is emitted to the environment as heat.
Halogen lamps
Halogen lamps offer a much higher illuminance than a standard light bulb using a whiter light, making colours far more perceivable by the human eye. Compactnes and a wide variety of these lamps offer huge possibilities for creative lighting. Halogen lamps make colours come to life and produce attractive shining effects. They remain bright at an even level during their entire life span, while being more energyefficient than standard light bulbs. For example, to achieve a luminous flux of 960 lumen a light bulb needs 75 W where a halogen lamp only needs 50 W.
Gas-discharge lamps
The basic principle of this lamp is the electric discharge. A current flows between two electrodes which allows a substance to emit light. This principle can take place using different types of metals or liquids.
High-intensity discharge (HIT) lamps distinguish themselves from light bulbs. They have an especially high light output in tiny spaces.
For example, a 2000 W HIT lamp that is placed within a football stadium emits as much light as two 5000 W light bulbs. On top of that, the light is produced on a surface that is no larger than a coin. A low amount of thermal radiation, incredible colour rendering and a long life span are benefits of modern HIT lamps. Because of the compact construction of the fixture the light can be aimed in a specific direction excellently. Because of this, HIT lamps are applied everywhere:
- When it comes to the presentation of goods and objects, like in shops.
- Where the amount of light and lifespan are important, like in factories, stadiums, street lighting and to illuminate plants.
Fluorescent lamps
All fluorescent lamps distinguish themselves by a high emittance of light, low power usage and a long lifespan. Cilinder shaped fluorescent lamps, live eight to twenty times longer than regular light bulbs and use up to 85% less electricity.
Compact fluorescent lamps work like fluorescent lamps, but don't take as much place. Mercury atoms are stimulated through an electric field between the electrodes to emit invisible UV light. Fluorescent powders on the inner sides of the tube transfer the UV radiation in visble light, where every powder generates a different colour. The benefits are:
- Saving 80 % energy opposed to a bright light bulb
- A life span 15 times longer than light bulbs
LED
Light Emitting Diodes are only a couple of millimeters in diameter, but have large technological benefits that make them a good alternative for conventionals lamps. They are semiconductors that transfer an electric current in to light. They emit red, orange, yellow, green of blue light. White light is created using a special LED technology
LED's give designers a large degree of liberty in creating innovative light. The many different colours, compact shapes and versatility of different modules all contribute to this.
Aside from its decorative qualities LED's use a low amount of power, have long lifespans and low maintenance costs. User fees are also low.
LED modules are used in the following applications:
- Illuminated denotations
- Design lamps
- Traffic lights
- Orientational lights in buildings
- Illuminating escape routes
- Recessed luminaires
- Signals
A LED is created from different layers of semiconductor materials. In contrast to light bulbs, LEDS emit one specific colour. The colour depends on the used materials, and goes from red to orange, yellow, green and finally blue. White light is made using luminescence. A blue LED excites a yellow emitting phosphorus, mixing both colours makes white light. The last couple of years have meant that LED efficiency has risen considerably. Depending on the colour 20lm/W and more can be achieved. Voltage drop depends on the colour and is between 2V and 4V at a current of 70mA.
Technology is developing rapidly and LED is no exception. Because of this reason it is possible that information that is provided within the product specifications has aged. Do not hesitate to contact us to learn about the correct light source of the time.
Influence of temperature
The light output of LED's declines when temperature rises. Yellow LED's are more sensitive to temperature than green LED's. Lower emittances of light as a consequence of high temperature is reversible and not a degradation. Maximum environmental temperatures are 100 degrees celcius, this temperature should not be exceeded.
LED modules are constructed from a collection of individual LED's, mounted on a PCB with active or passive power stabilization. Different kinds of module families have a lightconductor or a lens as an option. PCB's are rigid or flexible. Modules with flexible print make it possible to make three-dimensional lightconstructions.
| Light colour number Philips | Osram | New lamp coding | Colour rendering index | Colour temperature |
| 82 | 41 | 827 | 85 | 2700 K |
| 83 | 31 | 830 | 85 | 3000 K |
| 84 | 21 | 840 | 85 | 4000 K |
| – | 11 | 860 | 85 | 6000 K |
| 86 | – | 865 | 85 | 6500 K |
| 92 | – | 927 | 95/96 | 2700 K |
| 93 | 32 | 930 | 95/96 | 3000 K |
| 94 | 22 | 940 | 95/96 | 4000 K |
| 95 | 12 | 950 | 98 | 5000 K |
| 96 | 72 | 965 | 97 | 6500 K |
About Light sources and LED
Voorheen waren lichtbronnen onderverdeeld in de volgende hoofdgroepen:
- Light bulbs
- Halogen lamps
- Gas-discharge lamps
- Fluorescent lamps
- Special light sources and electrodeless lamps
- LED
Light bulbs
The German watchmaker Johan Heinrich Goebel came up with the light bulb in 1854. Thomas A. Edison then repurposed the idea in to a consumer product in 1879. The light in the light bulb originates from an electric current that sparks up a tungsten wire. About 5% of the electric energy is converted in to light. The rest is emitted to the environment as heat.
Halogen lamps
Halogen lamps offer a much higher illuminance than a standard light bulb using a whiter light, making colours far more perceivable by the human eye. Compactnes and a wide variety of these lamps offer huge possibilities for creative lighting. Halogen lamps make colours come to life and produce attractive shining effects. They remain bright at an even level during their entire life span, while being more energyefficient than standard light bulbs. For example, to achieve a luminous flux of 960 lumen a light bulb needs 75 W where a halogen lamp only needs 50 W.
Gas-discharge lamps
The basic principle of this lamp is the electric discharge. A current flows between two electrodes which allows a substance to emit light. This principle can take place using different types of metals or liquids.
High-intensity discharge (HIT) lamps distinguish themselves from light bulbs. They have an especially high light output in tiny spaces.
For example, a 2000 W HIT lamp that is placed within a football stadium emits as much light as two 5000 W light bulbs. On top of that, the light is produced on a surface that is no larger than a coin. A low amount of thermal radiation, incredible colour rendering and a long life span are benefits of modern HIT lamps. Because of the compact construction of the fixture the light can be aimed in a specific direction excellently. Because of this, HIT lamps are applied everywhere:
- When it comes to the presentation of goods and objects, like in shops.
- Where the amount of light and lifespan are important, like in factories, stadiums, street lighting and to illuminate plants.
Fluorescent lamps
All fluorescent lamps distinguish themselves by a high emittance of light, low power usage and a long lifespan. Cilinder shaped fluorescent lamps, live eight to twenty times longer than regular light bulbs and use up to 85% less electricity.
Compact fluorescent lamps work like fluorescent lamps, but don't take as much place. Mercury atoms are stimulated through an electric field between the electrodes to emit invisible UV light. Fluorescent powders on the inner sides of the tube transfer the UV radiation in visble light, where every powder generates a different colour. The benefits are:
- Saving 80 % energy opposed to a bright light bulb
- A life span 15 times longer than light bulbs
LED
Light Emitting Diodes are only a couple of millimeters in diameter, but have large technological benefits that make them a good alternative for conventionals lamps. They are semiconductors that transfer an electric current in to light. They emit red, orange, yellow, green of blue light. White light is created using a special LED technology
LED's give designers a large degree of liberty in creating innovative light. The many different colours, compact shapes and versatility of different modules all contribute to this.
Aside from its decorative qualities LED's use a low amount of power, have long lifespans and low maintenance costs. User fees are also low.
LED modules are used in the following applications:
- Illuminated denotations
- Design lamps
- Traffic lights
- Orientational lights in buildings
- Illuminating escape routes
- Recessed luminaires
- Signals
A LED is created from different layers of semiconductor materials. In contrast to light bulbs, LEDS emit one specific colour. The colour depends on the used materials, and goes from red to orange, yellow, green and finally blue. White light is made using luminescence. A blue LED excites a yellow emitting phosphorus, mixing both colours makes white light. The last couple of years have meant that LED efficiency has risen considerably. Depending on the colour 20lm/W and more can be achieved. Voltage drop depends on the colour and is between 2V and 4V at a current of 70mA.
Influence of temperature
The light output of LED's declines when temperature rises. Yellow LED's are more sensitive to temperature than green LED's. Lower emittances of light as a consequence of high temperature is reversible and not a degradation. Maximum environmental temperatures are 100 degrees celcius, this temperature should not be exceeded.
LED modules are constructed from a collection of individual LED's, mounted on a PCB with active or passive power stabilization. Different kinds of module families have a lightconductor or a lens as an option. PCB's are rigid or flexible. Modules with flexible print make it possible to make three-dimensional lightconstructions.
| Light colour number Philips | Osram | New lamp coding | Colour rendering index | Colour temperature |
| 82 | 41 | 827 | 85 | 2700 K |
| 83 | 31 | 830 | 85 | 3000 K |
| 84 | 21 | 840 | 85 | 4000 K |
| – | 11 | 860 | 85 | 6000 K |
| 86 | – | 865 | 85 | 6500 K |
| 92 | – | 927 | 95/96 | 2700 K |
| 93 | 32 | 930 | 95/96 | 3000 K |
| 94 | 22 | 940 | 95/96 | 4000 K |
| 95 | 12 | 950 | 98 | 5000 K |
| 96 | 72 | 965 | 97 | 6500 K |
